|
Selecting Authentication Methods
On the Authentication page of the Settings dialog you can
define customized authentication methods. Two lists are displayed on the
page, one for general authentication, and the one below it for
authentication methods used in public-key authentication.
The icons displayed above the list can be used to add a new
authentication method, delete an existing authentication method, and move
the authentication methods upwards or downwards in the preference list.
Authentication methods higher up on the list will be tried first.
Usually authentication methods that require user interaction should be
tried last.
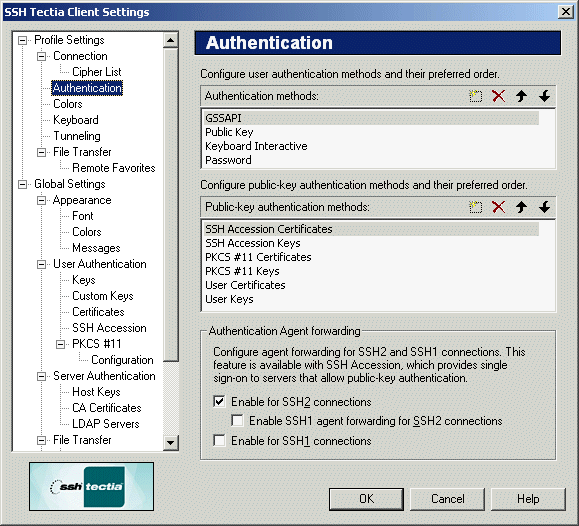
Figure : Defining the authentication settings
Authentication Methods
Possible methods for general authentication are the following:
- Password
Use a password for authentication.
- Public-Key
Use public-key authentication.
- Keyboard-Interactive
Keyboard-Interactive is designed to allow the Secure Shell client to support
several different types of authentication methods. For more information on
Keyboard-Interactive, see SSH Tectia Client/Server Product Description.
- GSSAPI
GSSAPI (Generic Security Service Application Programming Interface) is a
common security service interface that allows different security
mechanisms to be used via one interface. For more information on GSSAPI,
see Editing the Configuration Files
and SSH Tectia Client/Server Product Description.
- SecurID (legacy)
Using SecurID authentication requires that you have a SecurID device that
generates the numeric codes that are needed to log in. The legacy method
is supported for interoperability reasons. It is recommended to use the
Keyboard-Interactive method instead.
- PAM (legacy)
Use Pluggable Authentication Module (PAM) for authentication. PAM is an
authentication method that has gained wide popularity especially on Unix
platforms. The legacy method is supported for interoperability reasons. It
is recommended to use the Keyboard-Interactive method instead.
The default authentication methods are GSSAPI, public-key authentication,
Keyboard-Interactive, and password authentication.
Public-Key Authentication Methods
Possible methods for public-key authentication are the following:
- SSH Accession Certificates
Use SSH Accession certificates for authentication. SSH Accession Lite offers an
easy method for accessing authentication credentials on smart cards and
other hardware tokens. It can be also used as an authentication agent.
- SSH Accession Keys
Use SSH Accession keys for authentication. SSH Accession Lite offers an easy
method for accessing authentication credentials on smart cards and other
hardware tokens. It can be also used as an authentication agent.
- PKCS #11 Certificates
Authenticate by using PKCS #11 certificates (certificates stored for
example on a smart card or a USB token). For more information on using
PKCS #11 certificates, see Section Managing PKCS #11 Providers.
- PKCS #11 Keys
Authenticate by using PKCS #11 keys (keys stored for example on a
smart card or a USB token). For more information on using PKCS #11
keys, see Section Managing PKCS #11 Providers.
- User Certificates
Use user certificates for authentication. For more information on using
certificates, see Section Managing Certificates.
- User Keys
Use user keys for authentication. For more information on using user
keys, see Section Managing Keys.
Note: The automatically handled authentication methods should
always be listed first, meaning that public-key authentication should
precede password authentication. This way the automatically handled
method will be used whenever possible.
Authentication Agent Forwarding
An authentication agent is a program that makes authentication using
private keys automatic. SSH Accession Lite can provide agent
functionality for SSH Tectia Client.
The agent is automatically used for public-key authentication. This way,
you only have to type the passphrase of your private key once to the
agent. Furthermore, authentication data does not have to be stored on
any other machine than the local machine, and authentication passphrases
or private keys never go over the network.
Agent forwarding can be enabled or disabled on the basis of the Secure
Shell protocol used. Select the check box for any of the options you want
to use:
- Enable SSH2 connections
Select this check box to allow authentication agent forwarding to be used
for connections that use the Secure Shell version 2 protocol.
- Enable SSH1 agent forwarding for SSH2 connections
Select this check box to allow authentication agent forwarding with the
Secure Shell version 1 protocol to be used for connections that use the
Secure Shell version 2 protocol.
- Enable for SSH1 connections
Select this check box to allow authentication agent forwarding to be used for
connections that use the Secure Shell version 1 protocol.
 [Contents]
[Index]
[Contents]
[Index]
[ Contact Information | Support | Feedback | SSH Home Page | SSH Products ]
Copyright © 2010 SSH Communications Security Corp.
This software is protected by international copyright laws. All rights reserved.
Copyright Notice
|