
 |
Table of Contents
The Secure Shell protocol used by Tectia Server for IBM z/OS provides mutual authentication – the client authenticates the server and the server authenticates the client user. Both parties are assured of the identity of the other party.
The Secure Shell server host can authenticate itself using either traditional public-key authentication or certificate authentication.
Different methods can be used to authenticate Secure Shell client users. These authentication methods can be combined or used separately, depending on the level of functionality and security you want.
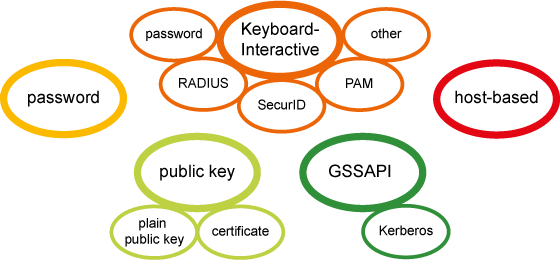
Figure 5.1. Secure Shell user authentication methods. Note that all of the methods are not available on z/OS.
Tectia Server for IBM z/OS allows public-key and password authentication by default. It also supports keyboard-interactive and host-based authentication.