Application Tunneling
Application tunneling, or port forwarding, is a way to tunnel otherwise
unsecured TCP traffic through Secure Shell. You can secure for example
POP3, SMTP, and HTTP connections that would otherwise be unsecured –
see Figure Encrypted Secure Shell tunnel.
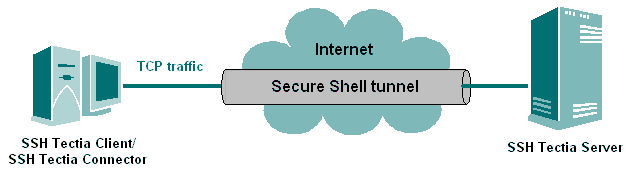
Figure : Encrypted Secure Shell tunnel
The Secure Shell v2 connection protocol provides channels that can be used for a wide
range of purposes. All of these channels are multiplexed into a single
encrypted tunnel and can be used for tunneling (forwarding) arbitrary
TCP/IP ports
and X11 connections
.
The client-server applications using the tunnel will carry out their own
authentication procedures, if any, the same way they would without the encrypted
tunnel.
The protocol/application might only be able to connect to a fixed port
number (e.g. IMAP 143). Otherwise any available port can be chosen for port
forwarding.
Privileged ports (below 1024) can be forwarded only with root privileges.