Outgoing Tunnels
Local port forwarding (an outgoing tunnel) forwards traffic coming to a local
port to a specified remote port.
Example: On Unix, when you issue the command
$ ssh2 -L 1234:localhost:23 username@host
all traffic coming to port 1234 on the client (localhost) will be
forwarded to port 23 on the server (host).
Note that the localhost definition will be resolved by the
SSH Tectia Server after the connection is established. In this case localhost
therefore refers to the server (host) itself.
Note: It is important to understand that if you have three hosts, client,
sshdserver, and appserver, and you forward the traffic coming to the
client's port x to the appserver's port y, only the
connection between the client and sshdserver will be secured. See
Figure Forwarding to a third host. The
command you use would be similar to the following:
$ ssh2 -L x:appserver:y username@sshdserver
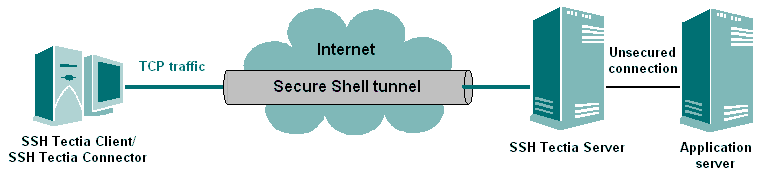
Figure : Forwarding to a third host
When using SSH Tectia Client on Windows, the tunneling settings can be made under
Profile Settings -> Tunneling.